Integration Using Global Variables #
MMDAgent-EX has an internal storage area for global variables. .fst scripts, .mdf configuration files, or messages can assign, modify, and read those values.
Global variables are a collection of key-value pairs. Below we explain how to assign and reference values.
Assignment in .mdf #
All pairs written in the following form are assigned to and retained as key-value entries in the global variables at startup.
KeyName=String
You can retrieve these settings later, and you can also define arbitrary key-value entries in the .mdf that are unrelated to built-in settings.
Referencing and assigning in .fst #
In .fst files you can reference a global variable anywhere using ${%KeyName}.
The value is evaluated not at .fst load time but at the moment that line is executed.
The example below assigns the value of the global variable with key “ModelName” as the first argument (model alias) of the MODEL_ADD message. (See the FST format documentation for details on variable handling in .fst.)
0 LOOP:
<eps> MODEL_ADD|${%ModelName}|...
You can also use the value itself as a condition, like this:
LOOP LOOP:
${%KeyName}==string SYNTH_START|mei|...
You can also assign values using the end-of-line additional fields.
0 LOOP:
...
<eps> MODEL_ADD|mei|... ${%KeyName}=string
Assigning via messages #
You can assign values by sending the KEYVALUE_SET message.
Binding with MODEL_BINDFACE #
As an alternative use of the
MODEL_BINDFACE message, you can bind a morph to a global variable instead of a fixed value. A bound morph is controlled by the value of the bound global variable, and the morph will follow and update in real time whenever the variable changes.
This lets you, for example, provide a specific morph’s value from a setting in the .mdf, or stream values from an external source via KEYVALUE_SET messages to control a morph in real time.
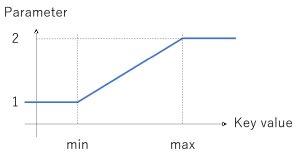
min and max are the minimum and maximum of the global variable’s value; rate1 and rate2 are the corresponding morph minimum and maximum values. Values below min are capped to rate1; values above max are capped to rate2. Values in between are linearly interpolated. The graph below illustrates this (horizontal axis = global variable value; vertical: 1 corresponds to rate1, 2 corresponds to rate2).
You can unbind with MODEL_UNBINDFACE.